Introduction [with
respect to software applications]
The current trend in the market towards 64-bit
computing on desktops has sparked interest in the industry for 64-bit
computers. Intel and AMD have already released their 64-bit processors suitable
for desktops and servers. However, 64-bit computers are not new; companies have
been using 64-bit systems on highend servers for years and they still do. What
is new is the interest in 64-bit computing for desktops. Microsoft’s Vista
operating system is expected to give a much needed fillip to the popularization
of 64-bit architectures.
With the advent of 64-bit versions of Linux and
Windows operating systems, there comes a huge challenge of porting applications
and device drivers. Is it necessary to port all applications? What kind of
applications require 64-bit computing horsepower and why? Can 32-bit
applications work on the 64-bit platforms? This paper tries to explore the
benefits of 64-bit to applications and answer some of the questions posed
above.
What is 64-bit
Computing?
“64-bit” computing implies computing on a 64-bit
processor. Simply put, the labels "16-bit," "32-bit",
"64-bit", etc., characterize a processor’s data stream. 64-bit wide
memory buses imply that the address lines are 64 bit wide and virtual
addressing mechanisms use 64 bit sized pointers. Although we hear the term "64-bit
code," it actually refers to code that operates on 64-bit data. It also
implies that by special instructions (or modes) one can access the 64-bit
registers or computing capability.
Figure:1 depicts a simplistic view of a processor
and the blocks that have to be 64-bit wide to be called a 64-bit processor.
|
64-bit Computing |

|
Why 64-bit?
This question is often not answered completely and
cannot be answered very quantitatively. Several factors determine if 64-bit
architecture will improve the performance of generic and everyday applications
or not.
64-bit architecture will definitely benefit those
applications that have one or more of requirements mentioned in this section.
Memory
A 32-bit machine utilizes 32 bits of virtual
addressing. It translates to a total virtual memory of 232 bytes which is 4 GB.
Often out of the 4 GB process address space, some space is reserved for the use
by the Operating System1. While 2 GB may be sufficient in many cases, corporate
databases have indexes that are definitely larger.
Graphic applications such as CAD, gaming
applications, multimedia and video editing software quickly consume RAM. With
the advent of DVD and HD_DVD and beyond, file sizes of 2 GB and more are becoming
common. Such huge file sizes cannot be supported easily in current 32 bit
systems (without performance penalties).
Simple applications like Web servers can also gain
significant performance improvements by loading static content into memory rather
than on slower disks. Performance of the 32 bit machine can be hindered owing to
the frequent swapping between the processes, when several processes (with large
memory requirements) execute concurrently.
Listed below are some applications that require high
memory:
▪ Graphic editors (CAD): Graphic editing software
is known to be memory hungry. Applications like Panaroma Factory (photo editing
software) are found to perform much better under higher virtual memory provided
by 64-bit processors.
▪ Video and multimedia editing software: The video
and audio editing software need higher memory because of the complex operations
they perform on a large data. 64-bit architecture helps these types of
applications with higher memory and processing power.
▪ Databases: Large organizations have large data
to be handled and higher memory provided by 64-bit architecture, most certainly
helps databases as they can store more information in memory compared to a
32-bit platform. This will result in higher performance databases.
The theoretical limit of memory in 64-bit systems
is 264 bytes which is 16 EB. Although systems with such a huge amount of memory
will be prohibitively expensive, the current systems provide 40 bits of
physical address space or 48 bits of virtual address space.
Large-number math
Large-number math is an obvious advantage offered
by a 64-bit processor. A 32-bit processor can handle the integer range of -2.1
billion to +2.1 billion (approximately). However, it is not to say that a
32-bit processor cannot handle a 64-bit number today. A number larger than
32-bits can be stored in multiple memory locations as lower and higher 32-bits
and the software can be programmed to treat it as a single 64-bit number (long long). But
these are at best workarounds and are not fast. On the other hand, a 64-bit
processor will be able to handle bigger numbers without having to resort to the
workarounds and hence are inherently faster.
This capability of the processor to handle larger
numbers helps the following cases:
▪ Large financial systems: These systems will work
with large numbers and 64-bit processor’s ability to work with larger numbers
comes in handy.
▪ Computer simulations: Computer simulations used
in medical field are extremely complex and require high performance processors.
64-bit processor with its mathematical ability with higher numbers.
▪ Graphics rendering (3D gaming): Computer
programs like Crafty (an open-source, high performance chess program) have
shown 47% improvement when run under 64-bit mode over 32-bit mode on AMD Athlon
processors.
▪ Compression, Cryptography (Encryption): Most of
the digital security systems are based on the algorithm used to encrypt the
data and the size of the keys (for encryption) used in the process. Larger keys
are safer and are harder to break. With 32-bit processors, 256-bit key will
need 8 addresses in memory (8 x 32 = 256 bit) and will involve more
mathematical computations. A 64-bit processor will store the same encryption
key in 4 addresses in memory and will significantly speed up the encryption
process.
Date Format
The current Date format is a 32-bit signed integer
which will expire soon2, hence the format has to be changed to 64 bit signed
integer. It is said that in Microsoft Windows environment a process cannot run for
more than 49.7 days. This is due to the limitation of 32 bit time format. The
system clock is used to evaluate the elapsed time (in milliseconds from the
inception) and this turns negative after 49.7 days.
What about normal
applications?
It is quite obvious that applications written to
exploit 64-bit architectures can gain from faster access to data, availability
of 64-bit resources like 64-bit and 128 bit registers, 64-bit pointers and
larger data types.
Applications can also have larger file caches and
map large process data in virtual address space and can support larger files
using standard system library calls, etc.
Categorically it cannot be stated that 64-bit
systems are better off for all scenarios, in certain cases the gains are not
significant (but they do measure up to 32 bit counterparts).
To port or not to
port?
The big question still remains unanswered and
ambiguous. The effort for porting all applications can be quite high and must
be balanced with a return-on-investment assessment. To ease the problems of
existing applications, most 64-bit architectures (operating system and
processor) operate in 2 modes – 64-bit mode and compatibility mode. 32-bit
applications can work without recompilation in the compatibility mode albeit with
some performance penalties. It is however advisable to port device drivers and
other performance sensitive applications to 64-bit and optimize the application
to make use of the enhancements provided by the 64-bit architecture.
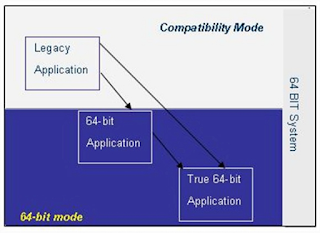
Above Figure shows what we foresee as the
evolution path for applications. Legacy 16-bit and 32-bit applications will
continue to exist. Some applications will just be compiled in 64-bit mode to
benefit from a few obvious advantages, while few others will be enhanced to
exploit the features of the 64-bit architecture.
Within the next 2-3 years we will see a lot more
proliferation of 64-bit desktop applications as 64-bit desktops and operating
systems, specifically from Microsoft appear and become popular in the market.
64-bit Drawbacks
Memory address values (called pointers) are now
twice as large and take up twice the space.
¾
Pointers normally take up a fraction of the space
in cache
¾
Now they are doubled in size and can squeeze out
other useful data from the cache and reduce performance.
¾
(slight improvement is to tag 64-bit integers
during programming e.g. REX mnemonic prefix, increase size < 10% for current
applications)
Conclusions
64-bit code can be compiled on 32-bit
architectures.
¾
64-bit data can be processed as two 32-bit
calculations although a performance penalty is incurred.
¾
Only applications designed to process 64-bit data
and are implemented on 64-bit hardware will achieve any speedup.
¾
On a daily basis we’re running into the Windows 2
GB barrier with our next-generation content development and pre-processing
tools.
¾
If cost-effective, backwards-compatible 64-bit
CPU’s were available today, we’d buy them today. We need them today.
The links where 64-bit Computing is discussed is
given below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-956UoImjn0&t=301s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s2aB13sOBi8
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/64-bit_computing
https://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia/term/64-bit-computing
https://www.webopedia.com/insights/64-bit-computing/
https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/64-bit-computing/
https://searchdatacenter.techtarget.com/definition/64-bit-processor
https://www.palisade.com/decisiontools_suite/64bit.asp
https://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2002/03/an-introduction-to-64-bit-computing-and-x86-64/
For all discussed seminar topics list click here Index.
…till next post, bye-bye and take care.


No comments:
Post a Comment