Let's introduce X-Vision, an incredible tool based on Augmented Reality (AR) that takes visualization to the next level. It brings real-time sensing capabilities to a tagged environment, aiming to boost productivity and enhance user-environment interaction. X-Vision works wonders in a range of settings, including factories, smart spaces, homes, offices, maintenance/facility rooms, and operation theaters.
Abstract:
X-Vision
revolves around an exceptional visualization tool based on Augmented Reality
(AR) that operates in a tagged environment. This article presents the design
and implementation of X-Vision, including the development of a physical
prototype that can project mind-blowing 3D holograms. These holograms are
encoded with real-time data, such as water level and temperature readings of
common office/household objects. Additionally, the article delves into the
quality metrics used to evaluate the performance of pose estimation algorithms,
which play a crucial role in reconstructing 3D object data.
Introduction:
The realm of
Augmented Reality (AR) has witnessed remarkable advancements driven by progress
in computer vision, connectivity, and mobile computing. We now encounter
various AR applications on a daily basis, such as Google Translate's augmented
display, AR GPS navigation apps, and CityViewAR for tourism. These applications
seamlessly bridge the physical and digital worlds by employing object
identification or providing information about the physical space. Visual
markers, 2D barcodes, and RFID tags serve as effective means to establish this
connection. Among these options, RFID tags stand out with their unique
advantages. They enable wireless communication within a short distance,
eliminating the need for line of sight. Moreover, RFID tags are cost-effective
and can be effortlessly attached to a wide range of inventory and consumer
products. By harnessing the power of RFID technology, X-Vision wirelessly
retrieves information about tagged object IDs and physical attributes, mapping
them to a captivating digital avatar.
AR-Based Smart Environment:
AR technology
seamlessly integrates digital components into our perception of the real world,
enabling interactive bidirectional communication and control between users and
objects across various domains. X-Vision falls into this exciting category by
combining object recognition, 3D pose estimation, and RFID sensing capabilities
to create a truly smart environment. Through the research and development of
X-Vision, we aim to amplify user-environment interaction and elevate user
experiences in areas such as education, tourism, and navigation.
Emerging RFID Applications:
RFID technology
has gained significant traction in industries for identification and tracking
purposes. Recent advancements have explored the fusion of RFID with computer
vision and AR technologies, paving the way for X-Vision's breakthrough.
X-Vision brings together these cutting-edge technologies for gaming, education,
and mixed reality applications. By leveraging RFID tags for object
identification and sensing, X-Vision unlocks the full potential of AR
technology, creating immersive and interactive experiences that leave a lasting
impact. Numerous studies have already showcased the effectiveness of AR and
RFID tags in gaming, education, and information display. In this article,
X-Vision not only utilizes RFID for object identification but also harnesses
its power for wireless sensing of the environment and object attributes. This
approach fosters a more intimate and comprehensive interaction between humans
and the objects that surround them.
Object
Identification and Pose Estimation:
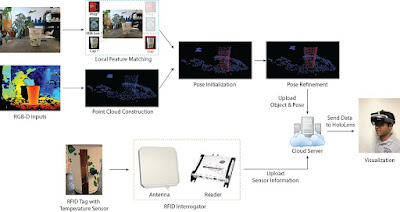
To bring
X-Vision to life, we employ an Intel RealSense D415 depth camera, capturing
color and depth information. This camera is seamlessly integrated with a
HoloLens device, enabling a powerful visual experience. The system utilizes
advanced local feature-based object recognition algorithms to identify objects
from a vast database. Once identified, the X-Vision system performs 3D pose
estimation using the Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithm, aligning point
clouds for accurate reconstruction. This dynamic combination of object
identification and pose estimation empowers X-Vision to render augmented
information with utmost precision.
RFID Sensing:
X-Vision
operates within an office space equipped with state-of-the-art RFID
infrastructure for conducting experiments. The system relies on Impinj Speedway
Revolution RFID readers, expertly connected to circularly polarized Laird
Antennas. We utilize Smartrac's paper RFID tags with Monza 5 IC, which serve as
backscattered-signal-based water level sensors. In addition, we employ
custom-designed tags equipped with EM 4325 IC to function as temperature
sensors. To interface with RFID readers and collect tag data, we implement the
Low Level Reader Protocol (LLRP) over the Sllurp Python library. We thoroughly
evaluate the performance of the RFID sensing system, taking into account
factors such as tag-reader separation and normalized RSSI scores. Through
rigorous study, we establish the working ranges between the camera and target
objects, as well as between tagged objects and readers. This ensures reliable
visualization and top-notch sensing quality.
Conclusion:
Prepare to be
amazed by X-Vision, an unparalleled augmented vision system that seamlessly
overlays physical objects with 3D holograms. These holograms are encoded with
valuable sensing information captured from tag sensors attached to everyday
objects. In this article, we showcase the remarkable capabilities of X-Vision
through two testing cases: water level sensing and temperature sensing.
Additionally, we conduct experiments to evaluate the pose estimation pipeline
and determine the working range of the system. The research and development of
X-Vision offer immense promise in revolutionizing various domains and enhancing
user experiences through the seamless integration of augmented reality, object
recognition, and RFID sensing technologies.
Hashtag/Keyword/Labels:
#XVision #AugmentedReality #RFID
#ObjectRecognition #PoseEstimation #SmartEnvironment
References/Resources:
1. Sun, Y., Kantareddy, S.N.R.,
Bhattacharyya, R., & Sarma, S.E. (2017). X-Vision: An Enhanced Augmented
Reality Visualization Tool. Auto-ID Labs, MIT.
2. Agrawal, A., Anderson, G.J., Shi, M.,
& Chierichetti, R. (2018). Tangible play surface using passive RFID sensor
array. CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems.
3. Ayala, A., Guerrero, G., Mateu, J.,
Casades, L., & Alam´an, X. (2015). Virtual touch flystick and primbox: Two
case studies of mixed reality for teaching geometry. International Conference
on Ubiquitous Computing and Ambient Intelligence.
For more such Seminar articles click index
– Computer Science Seminar Articles list-2023.
[All images are taken from Google
Search or respective reference sites.]
…till
next post, bye-bye and take care.



No comments:
Post a Comment